shunt dysfunction assessment*
* based on preliminary analysis of a dataset of 35 subjects focused on shunt dysfunction diagnosis.
benefits
- Non-Invasive Monitoring: Offers a safe, quick, and patient-friendly approach for point-of-care assessments.
- Real-time Trends: ICP dynamics over positional changes using changes in intracranial pressure (ICP) waveform parameters.
- Individualized: personalized information to your non-invasive toolkit
- Support Decisions: Provides additional data to aid in shunt dysfunction analysis.
ideal patient
Patients with suspicion of shunt dysfunction.
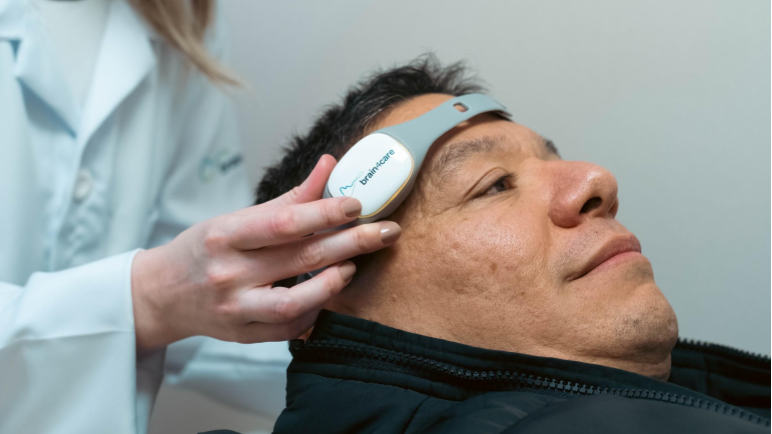
workflow
Monitor ICP dynamics in three distinct positions
- Laying down – for 5 min
- Supine 30 degrees – for 5 min
- Standing up – for 5 min
- Note shunt type, position and revisions
Relevant information to include as observations in the mobile App.
- Sensor and patient position
- Sensor and patient positioning events (displacement, excessive movement,
loss of waveform after positionings, etc…) - Any relevant symptoms and observations (headache increased when changing position)
data interpretation*
- Stable ΔP2/P1 ratio, a variation of less than 0.3 points during positional changes suggest shunt proper function
- Unstable ΔP2/P1 ratio, a variation of more than 0.3 points during positional changes suggest shunt dysfunction where:
- Underdrainage – high P2/P1 average ratios (> 1.3) and high maximum P2/P1 ratio of up to 1.5
- Overdrainage – ΔP2/P1 variation of more than 0.4 points between positional changes and significant P2/P1 ratio drops with worsening of symptoms when transitioning from lying to standing
